
Role-Based Access Management Made Simple
Role-Based Access Management (RBAC) is a strategic approach to controlling access within your organization. This approach ensures that individuals can only access resources essential for their specific job functions. By doing so, RBAC enhances security by minimizing unauthorized access and boosts operational efficiency by streamlining access management. This method effectively balances security needs with user convenience, ensuring that only the necessary permissions are granted for optimal organizational performance.
Understanding Role-Based Access Management
Role Management is an efficient approach to access control that assigns roles to groups rather than individuals. By linking specific job functions or responsibilities to predefined permission sets, Role Management ensures that employees have access only to the resources necessary for their roles.
This method enhances security by limiting elevated privileges and simplifies access management, allowing administrators to easily grant or revoke access for entire groups. It also supports compliance efforts with a clear framework for access control policies and audit trails, aligning access rights with business needs and regulatory requirements.
Key Activities in Role Management:
- Assigning and defining new roles with corresponding rules
- Periodically updating and reviewing Security Entitlements
- Modifying role definitions and assignments as needed
- Removing outdated roles
- Reviewing and updating user lists per role
- Developing and maintaining roles through analysis of existing user data, security entitlements, and identity attributes
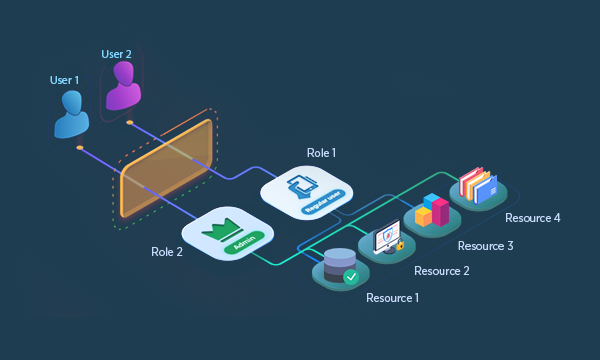
How Role Management Streamlines Access Control
Developing a role-based access management system involves integrating analytics to group users with similar identity attributes or entitlements. IAM systems enforce role models and periodically compare real-time user rights against predicted role models, addressing deviations automatically or escalating them for approval or denial.

Types of Role-based Access Management Practices:
Roles may need to be deleted or modified as circumstances change:
- Changing the user associated with a role
- Modifying policies associated with specific roles
- Adjusting session durations for roles
- Deleting roles that are no longer in use
By effectively managing the lifecycle of user identities and implementing robust access controls, organizations can ensure the security and integrity of their systems while facilitating efficient access management for their workforce.
Enhanced Access Control
Discover the Power of
Role Based Access
An RBAC solution streamlines access management with precise role creation, granular permission assignment, and automated workflows. It features real-time access monitoring, scalable architecture, and advanced reporting for efficient, secure, and compliant access control tailored to organizational needs.
Role-Based Permission
- Grants access based on user roles, ensuring that individuals receive the appropriate level of access aligned with their job responsibilities.
Granular Permission Assignment
- Assign permissions at a role level to ensure users have the appropriate access based on their role.
Automated Role Management
- Simplifies the creation, modification, and revocation of roles and permissions through automated workflows, reducing the complexity of manual access management.
How Avancer Helps
Avancer provides comprehensive support in Role Management by:
Precise Access Control
Defines roles by job functions and assigns permissions, ensuring users access only necessary resources.
Simplified User Management
Organizes access through roles to simplify management, reduce administrative overhead and minimize errors.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Enforces access controls aligned with security policies, ensuring compliance by granting minimal necessary privileges.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scales effortlessly with organizational growth, adapting to new roles and users while maintaining security.
